The travel of a sedate inside the human body—its retention, conveyance, digestion system, and excretion (ADME)—is a complex move of chemistry and science known as pharmacokinetics (PK). Central to this prepare, and frequently ignored in casual talk, is a apparently straightforward however significantly critical parameter: the Blood-to-Plasma Concentration Proportion (Rb). Characterized as the concentration of the medicate in entire blood (Cblood) isolated by its concentration in plasma (Cplasma), this proportion is a significant determinant of a drug’s extreme destiny and its restorative efficacy.
Background and Pharmacokinetic Significance
For decades, plasma has been the favored natural framework for measuring medicate concentration in PK considers. The method of reasoning is commonsense: plasma is generally homogenous, making it less demanding to store and analyze than entire blood, and it’s accepted that the concentration of the sedate in plasma is in harmony with, and subsequently reflects, the concentration at the location of action.
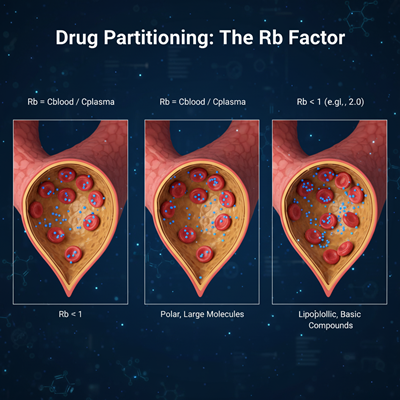
However, this presumption holds genuine as it were when the medicate does not specially tie to or segment into the cellular components of blood, basically ruddy blood cells (erythrocytes). The Rb esteem specifically measures this partitioning:
- Rb≈1: The medicate disperses similarly between ruddy blood cells and plasma. Plasma-based PK parameters are for the most part representative.
- Rb<1 (e.g., 0.5): The sedate has a moo liking for blood cells and is concentrated more in the plasma. This is commonplace for profoundly polar, huge molecules.
- Rb>1 (e.g., 2.0): The sedate has a tall fondness for and amasses inside the blood cells. This is frequently the case for lipophilic, fundamental compounds.
Impact on Clearance and Volume of Distribution
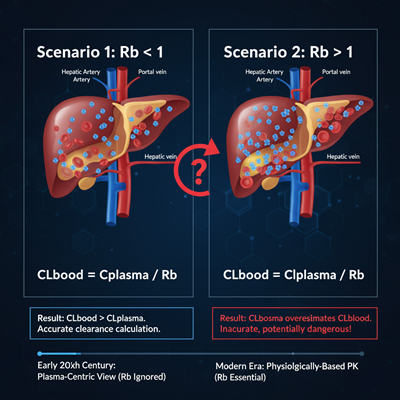
The Rb is basic for precisely calculating key PK parameters, especially clearance (CL). Pharmacokinetic models regularly calculate plasma clearance (CLplasma), which must be changed over to blood clearance (CLblood) for physiological pertinence, particularly when considering organ blood stream (e.g., hepatic clearance).
CLblood=CLplasma/Rb
If a medicate has an Rb>1 and a tall plasma clearance is measured, the calculated CLplasma may essentially overestimate the genuine hepatic clearance, possibly indeed surpassing the hypothetical greatest, which is the real hepatic blood stream. An precise Rb is in this manner crucial for foreseeing organ-specific digestion system and elimination.
Furthermore, the Rb impacts the clear Volume of Dispersion (Vd), a parameter reflecting how broadly a sedate conveys into body tissues. Contrasts in blood dividing contribute to the generally tissue dispersion profile.
Historical Setting: The Plasma Worldview Shift
The noticeable quality of plasma estimations is generally a item of chronicled limitations. In the early to mid-20th century, expository strategies were less touchy, and the down to earth challenges of working with entire blood—which clots and is heterogeneous—made plasma a distant more sensible test. Thus, the field of clinical pharmacokinetics created intensely around the presumption of plasma-centric medicate distribution.
However, as pharmaceutical science progressed, and especially with the rise of touchy explanatory strategies like Fluid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), errors started to develop. Analysts watched that for certain classes of compounds, particularly fundamental and lipophilic drugs, plasma concentrations alone were deceiving. This driven to a basic re-evaluation, pushing the Rb from an cloud exploratory esteem to a required early-stage medicate advancement parameter, giving a interface between the unbound medicate division in plasma and its generally concentration in the circulation.
Current Patterns: Forecast and Modeling
Today, the center in medicate improvement is on foreseeing the Rb as early as conceivable. Exploratory assurance through in vitro hatching with new entire blood is the gold standard, but computational strategies are progressively prevalent.
Mechanistic and Computational Approaches
- Quantitative Structure-Activity/Property Connections (QSAR/QSPkR): Analysts are creating models that utilize atomic descriptors (e.g., lipophilicity/LogP, ionization/pKa, plasma protein official) to foresee Rb. These models frequently utilize progressed factual strategies, counting Manufactured Neural Systems (ANNs), and are prepared on huge datasets of exploratory Rb values.
- Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling: PBPK models are modern computer reenactments that utilize physiological parameters (like blood streams, organ volumes, and tissue composition) along with drug-specific parameters, counting Rb, to foresee the whole time course of sedate concentration in all major organs and tissues. An exact Rb is a principal input for these models to accurately relate organ-to-plasma proportions (Kp) to tissue distribution.
Dried Blood Spots (DBS)
A eminent mechanical slant is the utilize of Dried Blood Spots (DBS) for test collection. DBS employments entire blood, making the Rb esteem intrinsically basic for information elucidation. Since DBS offers points of interest in test collection (negligible volume, simple capacity), exact Rb assurance is key to dependably interpreting whole-blood DBS information back to plasma concentrations utilized for conventional PK investigation and restorative medicate monitoring.
Expert Suppositions and Implications
Pharmaceutical researchers all around concur that ignoring Rb can lead to exorbitant late-stage disappointments and, more basically, unseemly dosing regimens in the clinic.
“The Blood-to-Plasma Proportion is an irreplaceable device for deconvoluting the physiological pertinence of plasma clearance,” states one pharmacokinetics master. “In case a medicate intensely allotments into ruddy blood cells, utilizing plasma clearance alone can lead to the incorrect conclusion that the sedate is dispensed with at an outlandishly quick rate, possibly slowing down a promising compound.”
Implications for Medicate Advancement and Persistent Safety
- Optimized Dosing Regimens: A exact Rb permits for the calculation of the adjust blood clearance, driving to more exact forecasts of a drug’s half-life and the time required to reach steady-state concentrations. This straightforwardly illuminates the ideal measurements and recurrence for patients, making strides both viability and safety.
- Poisonous quality and Off-Target Impacts: A tall Rb may recommend a noteworthy concentration of the medicate inside the blood compartment, which might have suggestions for hemotoxicity (poisonous quality to blood cells). Alternately, a exceptionally moo Rb implies more medicate is free in the plasma, possibly expanding its accessibility for systemic dispersion and off-target side effects.
- Blood as the Favored Framework: For drugs with a exceptionally tall Rb, entirety blood, or maybe than plasma, may be the predominant network for medicate checking, as it gives a more steady and agent degree of add up to systemic exposure.
In rundown, the Rb is distant from a simple scholarly interest. It is a principal physiological checkpoint that joins a drug’s physicochemical properties to its complex in vivo behavior. As medicate revelation moves toward computational and miniaturized examining strategies, the precise assurance and forecast of the Blood-to-Plasma Proportion will proceed to be a foundation of present day, physiologically-informed pharmacokinetics.